Output
All available output formats are provided on this page.
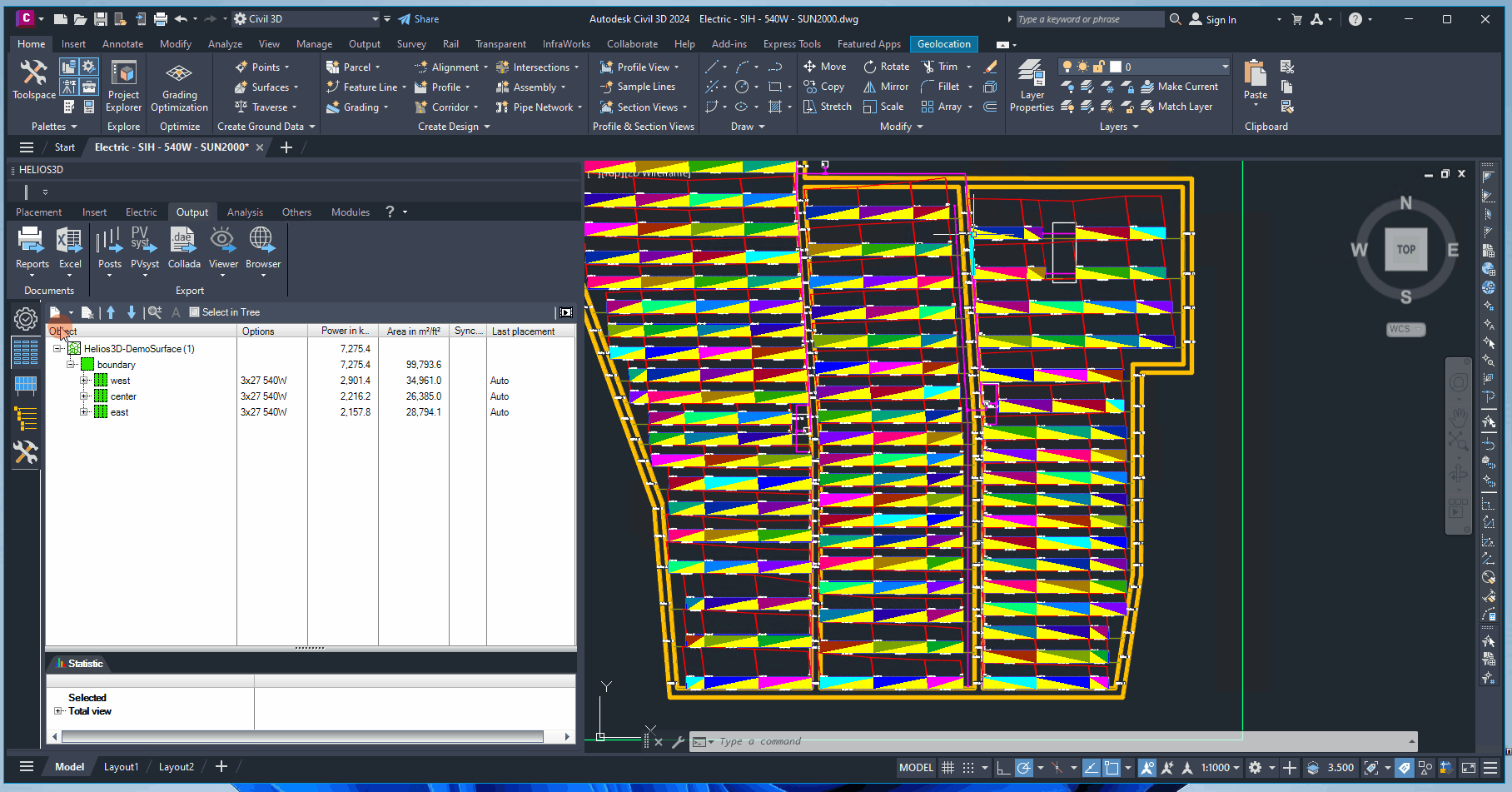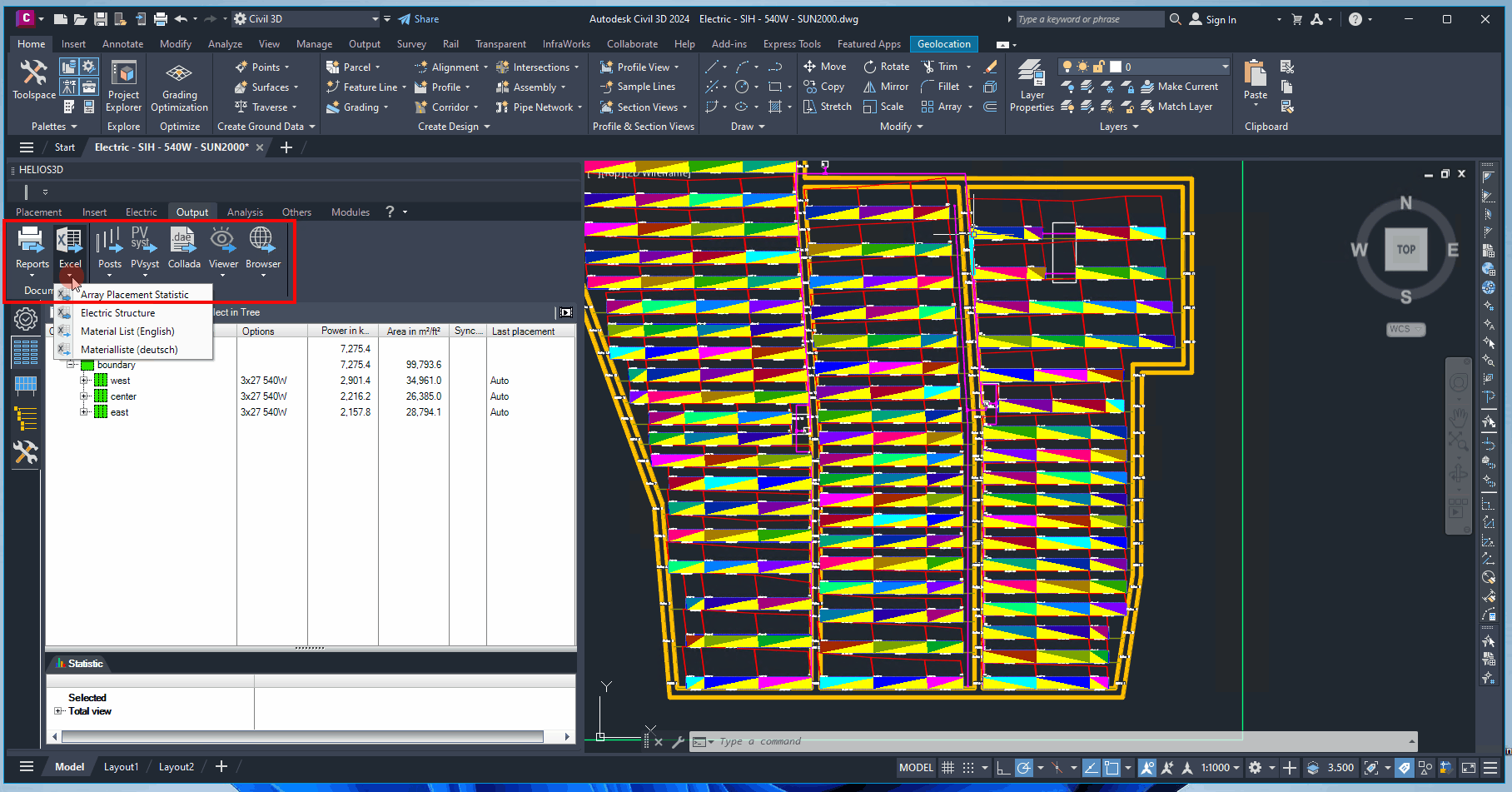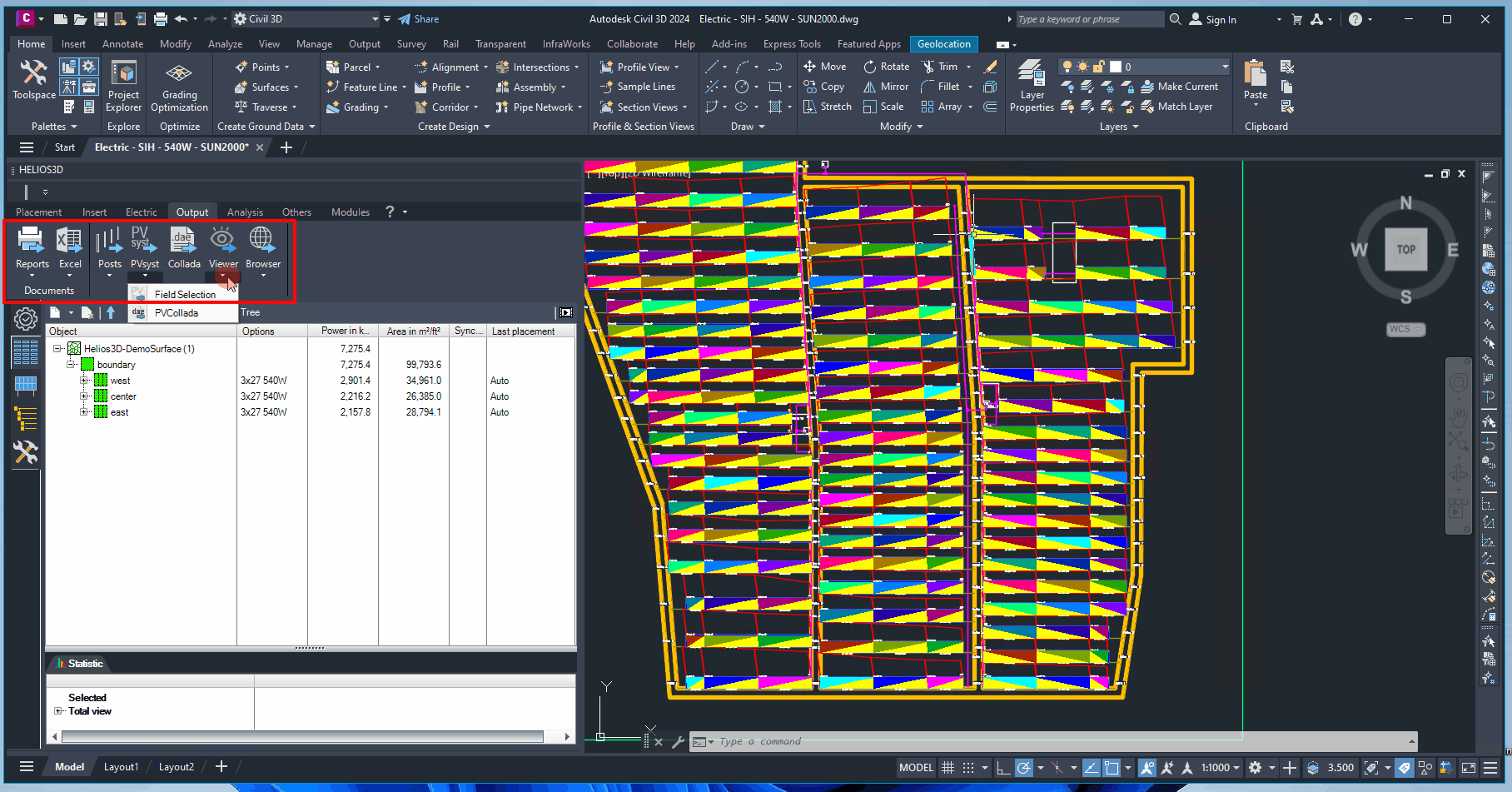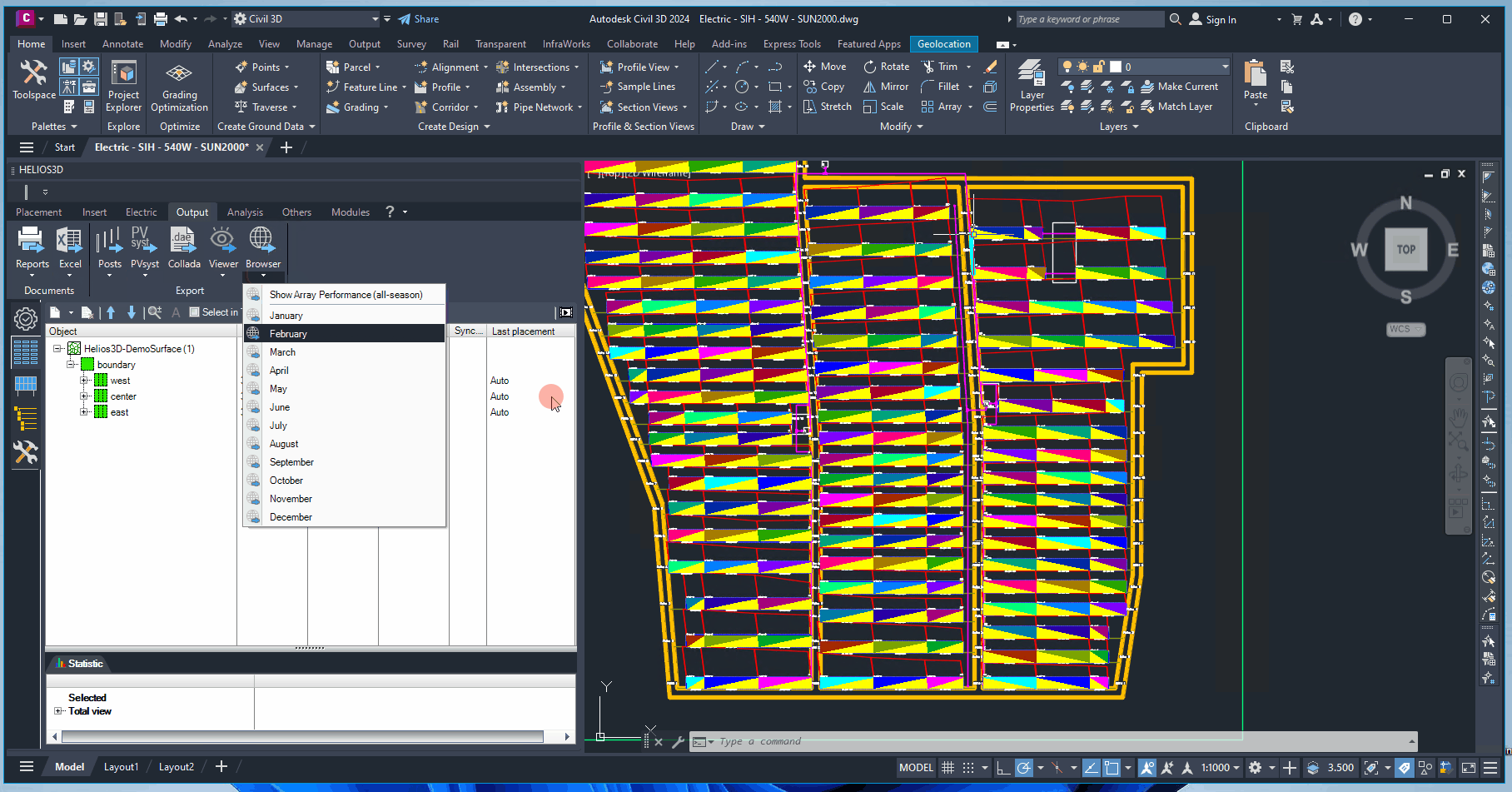
Command Group Documents
Print Reports

This section includes various reports that can be generated for the current drawing and then saved in external formats, such as PDF or Excel. The available reports are: Project Overview, Post Report, Cable List, and Electrical Structure.
Print Project Overview

Opens the print dialog with the project overview report.
Print Post List

Opens the print dialog for the post list.
Print Cable List

Opens the print dialog for the cable list.
Print Electrical Structure

Opens the print dialog for the Electrical Structure.
Excel Exports
Offers various formats for generating Excel lists.
Export Array Placement Statistic

Saves the placement statistic for the node selected in the placement structure tree. Fields or areas or DTMs can be selected and for multi-selection, only nodes with the same parent are allowed.
Export extended placement statistic with tables

Saves the extended placement statistic for the node selected in the placement structure tree. An entry for any PV table insertion is added to the row entries on the second page. Fields or areas or DTMs can be selected and for multi-selection, only nodes with the same parent are allowed.
Export Electric Structure Tree

Exports the structure tree for the electric placement into an Excel file. The result file matches the display of the „Electric Structure“ view including the cable losses. The exports always show each structure tree on a separate sheet, but in the same document.
Export cable connections to Excel
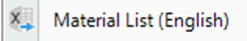

Generates sheets for string cables and cable connections between devices.
Command Group Export
Export Post List
This section provides three functions for exporting drawing data to different programs.
- Post List Export: Exports the post list into a C3D file. This file type is a plain text format and can be edited with any text editor.
- Data Format: The exported data is stored in the following structure:
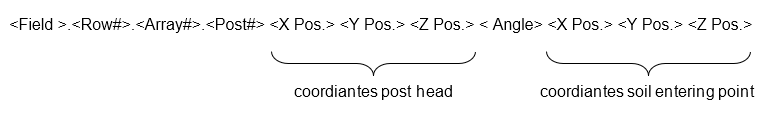
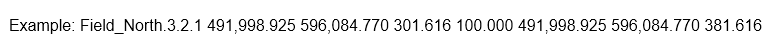
The provided data excerpt represents the first post in the second rack (array) of the third row in „Field_North“ (with spaces replaced by underscores).
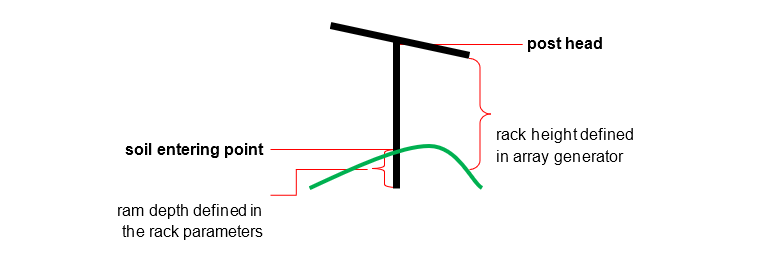
- X-, Y-, and Z-Values: These values specify the insertion point of the post in world coordinates (WCS) and correspond to the starting point (post head) of the line that visually represents the post.
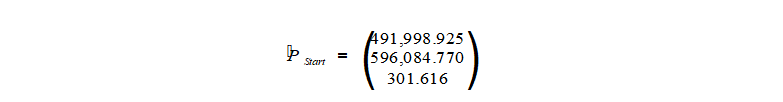
The rotation of the post in our example is 100 Gon.
The X-, Y- and Z-values behind the rotation angle mean the entering point to the soil.
The simple graphic below shows the meaning of the two points from export file entries.
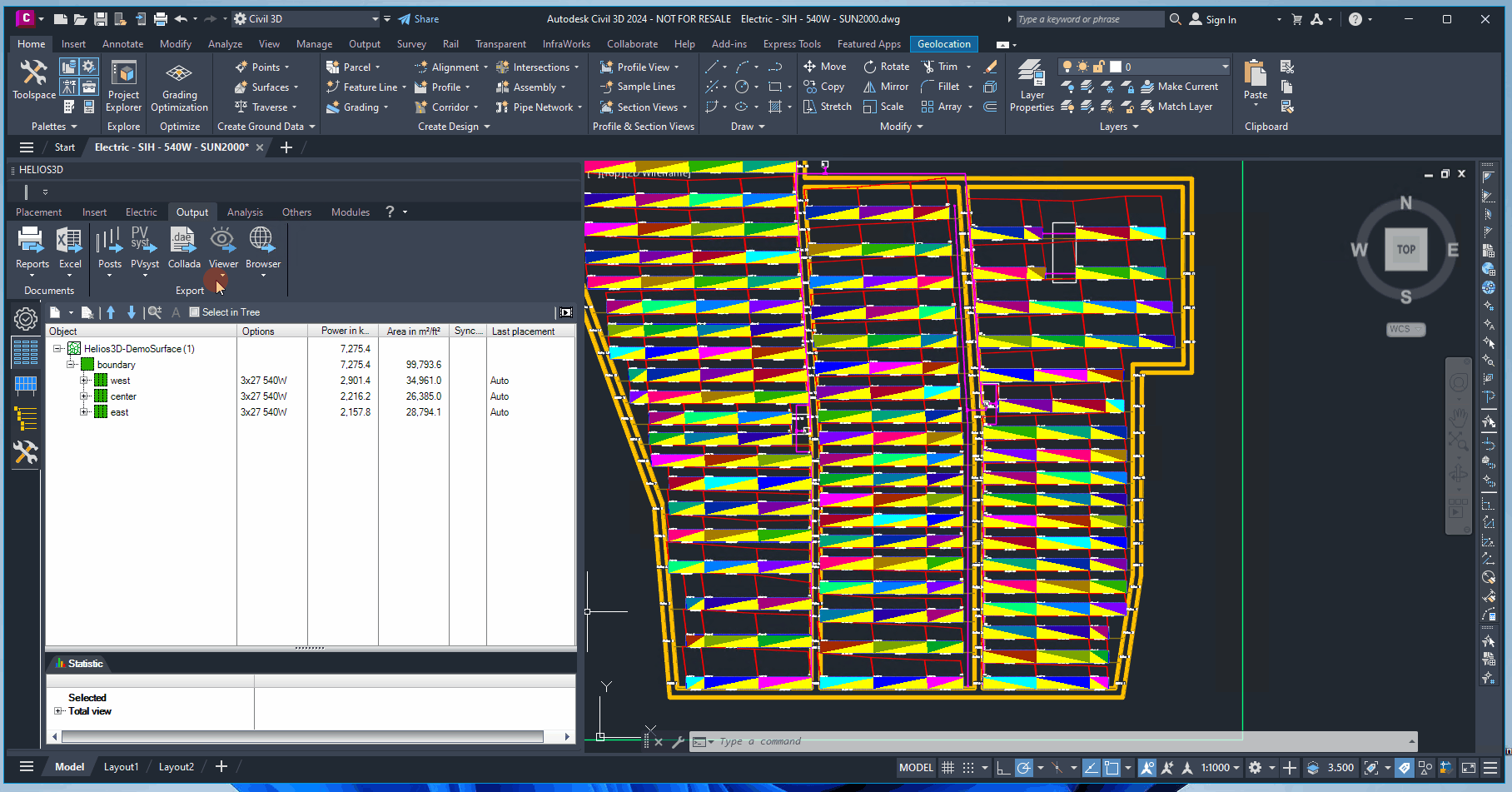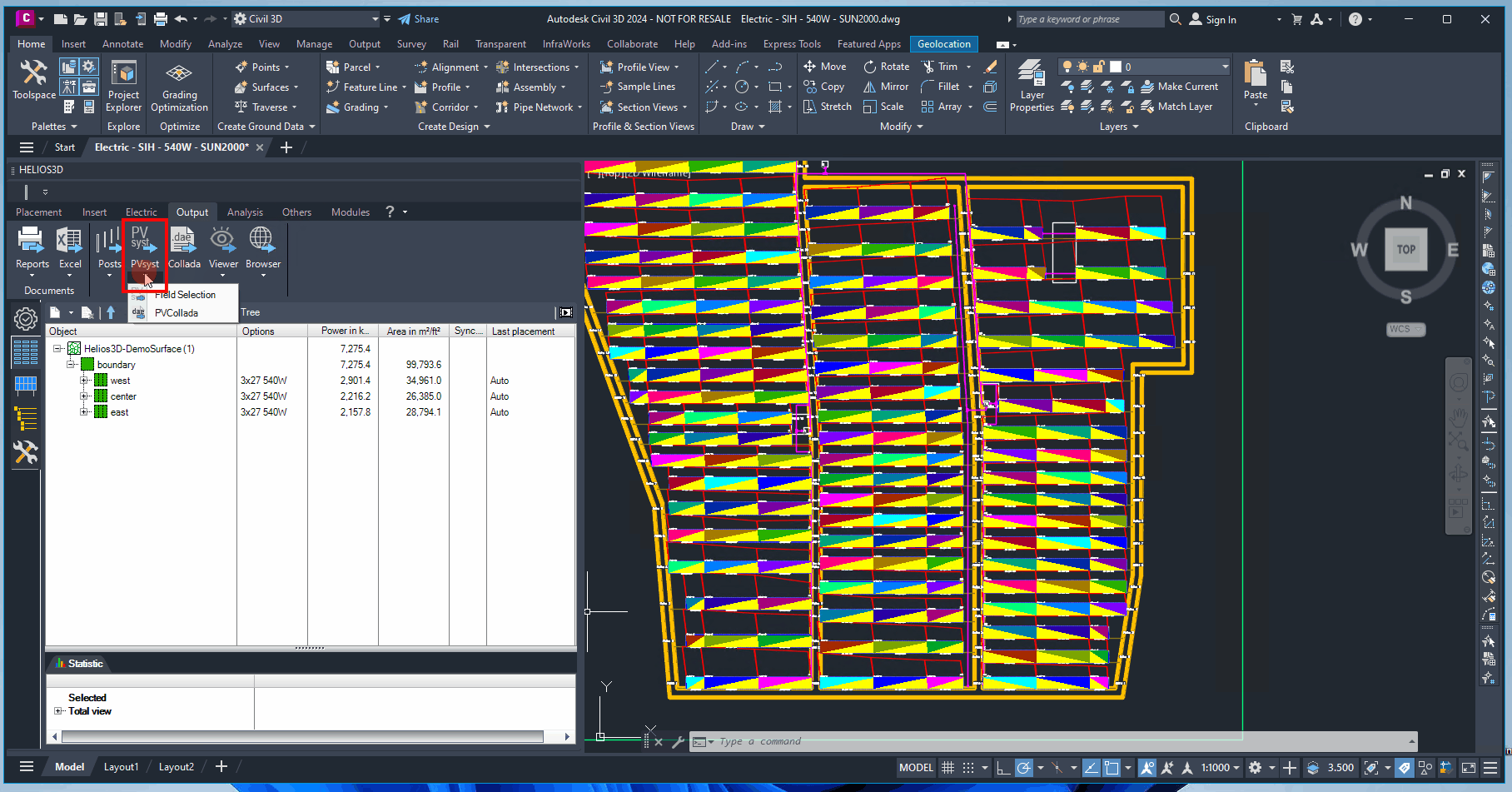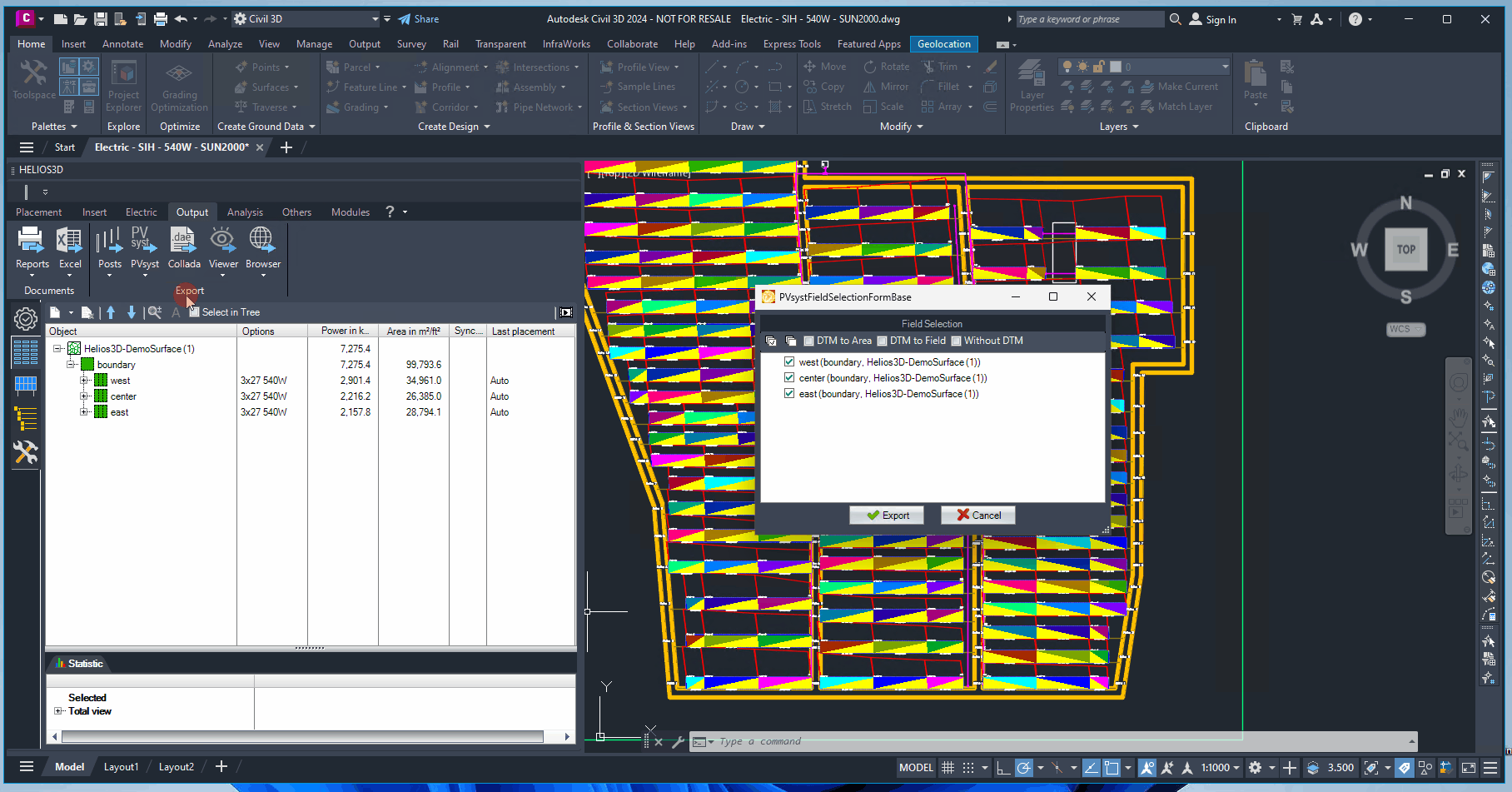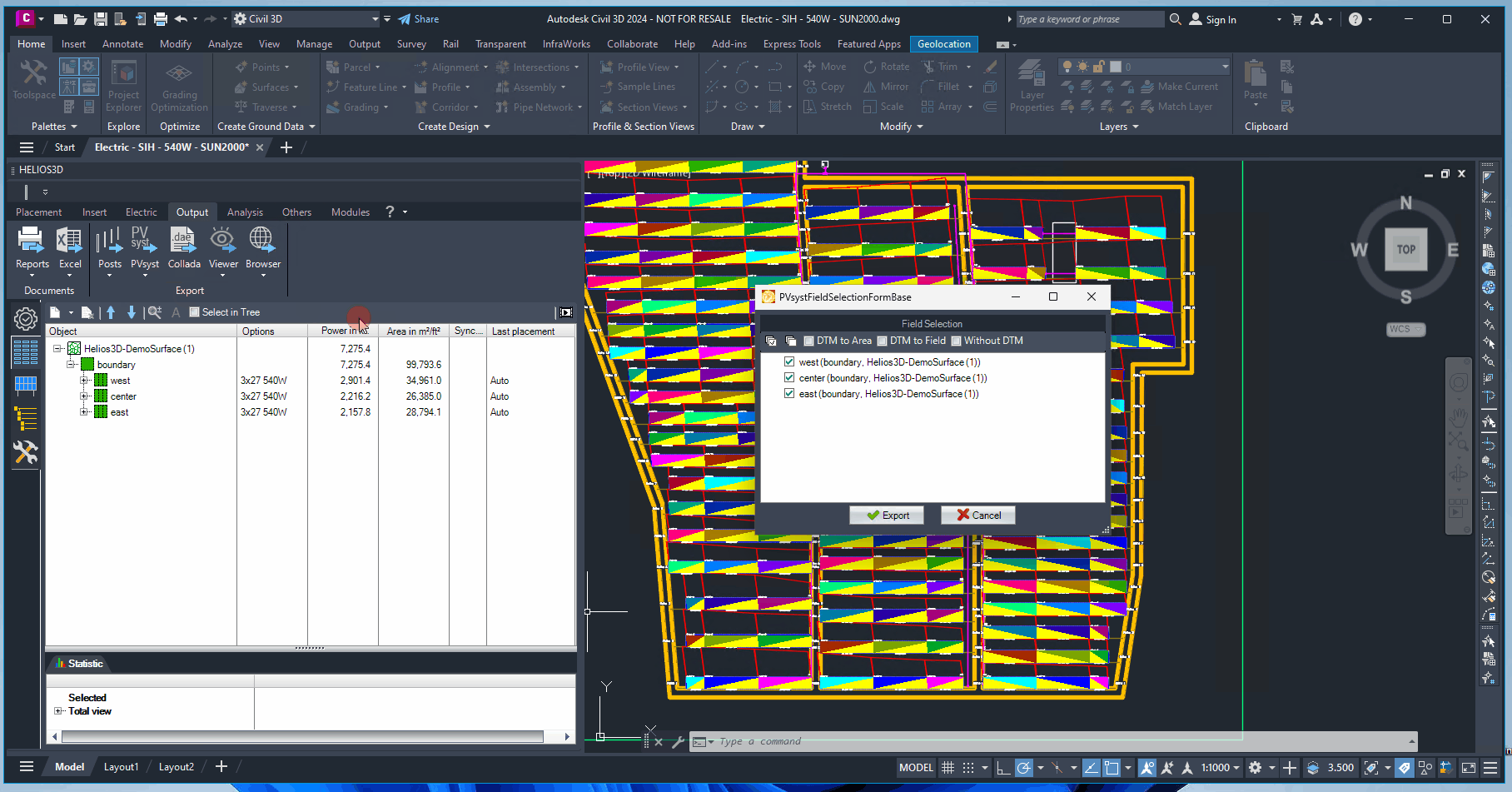
PVsyst Export

Exports the surfaces of a Digital Terrain Model (DTM), the photovoltaic active planes of the modules, and shadow objects into a text file with the extension *.H2P. This file can be imported into PVsyst for shadow analysis and profit calculations.
Export with Field Selection
Calls the PVsyst export with an additional dialog before the final export. In that dialog you can explicitly select those fields that should be exported, so the data set will be reduced.
Clicking the export button exports the entire drawing. Alternatively, clicking the small arrow on the right opens a dialog box where you can select specific fields for export. Additionally, you can restrict the export of surface triangles to designated area or field boundaries using the relevant checkboxes.
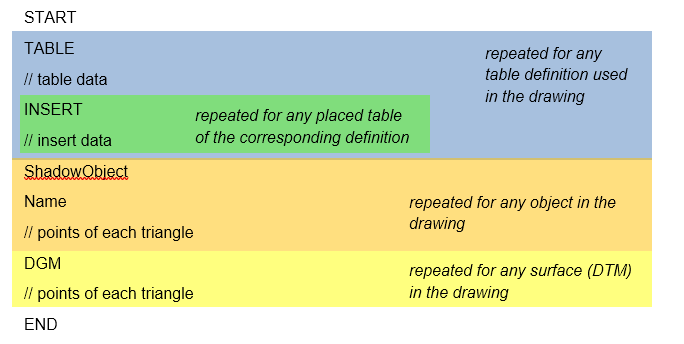
Format Description:
The document is structured with the keywords START and END marking its beginning and end, respectively. The content within follows this schema:
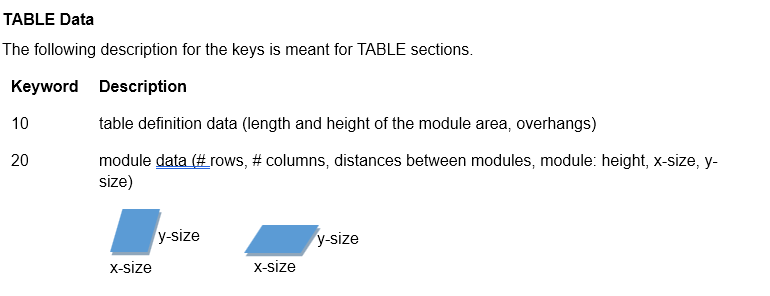

The table definition data is structured as follows:
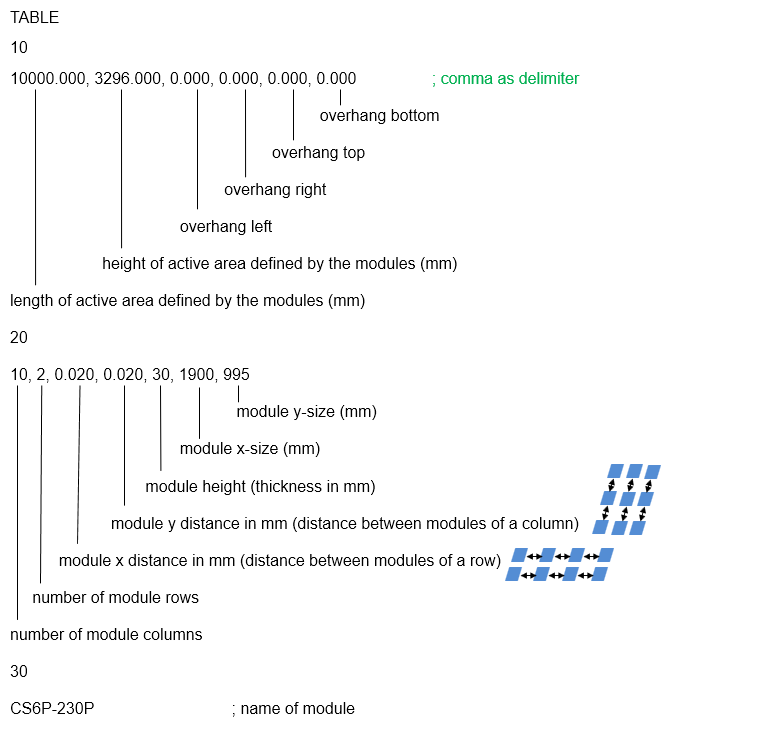
INSERT Data
The following description for the keys is meant for INSERT sections.
| Keyword | Description |
| 10 | 3D coordinate of the insertion point |
| 50 | azimuth |
| 55 | slope angle |
| 56 | module inclination |
The structure of the insert data looks as follows:
INSERT
10
0.000, 0.000, 0.000 ; x, y, z
50
0.000 ; azimuth angle
55
-2.929 ; slope angle
56
30.000 ; inclination angle
Shadow Objects
We describe all shadow objects using triangles, as this provides a universal representation for all possible shapes. Customers can also create custom objects using specific AutoCAD mesh objects.
The structure of the shadow object data is organized as follows:

DGM (DTM / Surface) Data
In the DGM section, each line represents one triangle of the surface. The structure of each line is as follows:
Example for an Export File:
File Text: Comments:
START ; start flag of the file
TABLE ; definition of the dimensions of the first table follows
10 ; table definition data follows
6077.500,3337.800,0.000,0.052,0.039,0.039; length, height, overhang: left, right, top, bottom
20 ; module definition data follows
6,2,0.021,0.010,30,1900, 995 ; # columns, # rows, x distance, y distance, height, x, y
30 ; module name follows
Modul 160W 1638×983 ; module name
INSERT ; insertion information of the first table follows
10 ; insertion point follows
0.000,0.000,0.000 ; x, y, z
50 ; azimuth follows
0.000 ; angle in degrees
55 ; slope follows
1.586 ; angle in degrees
56 ; module inclination follows
30.000 ; angle in degrees
INSERT ; insertion information of the next table follows
…
TABLE ; definition of the dimensions of the next table follows
…
DGM ; definition of the first DTM / surface follows
-110.993,-46.527,6.374;-107.054,-42.001,6.179;-107.095,-39.147,6.046 ; first triangle
-110.993,-46.527,6.374;-107.095,-39.147,6.046;-115.288,-46.527,6.680 ; second triangle
…
DGM ; definition of the next DTM / surface follows
…
END ; end flag of the file (confirms the valid ending)
Export scene to COLLADA format
Opens the dialogue to export the drawing to the .dae format. The objects that should be included can be chosen freely by that. COLLADA is an XML-based open exchange format for 3D data between different 3D applications.
PVsyst is one application that can read this format.
COLLADA is an XML-based open exchange format designed for transferring 3D data between different 3D applications. PVsyst is one such application that can read and utilize this format.
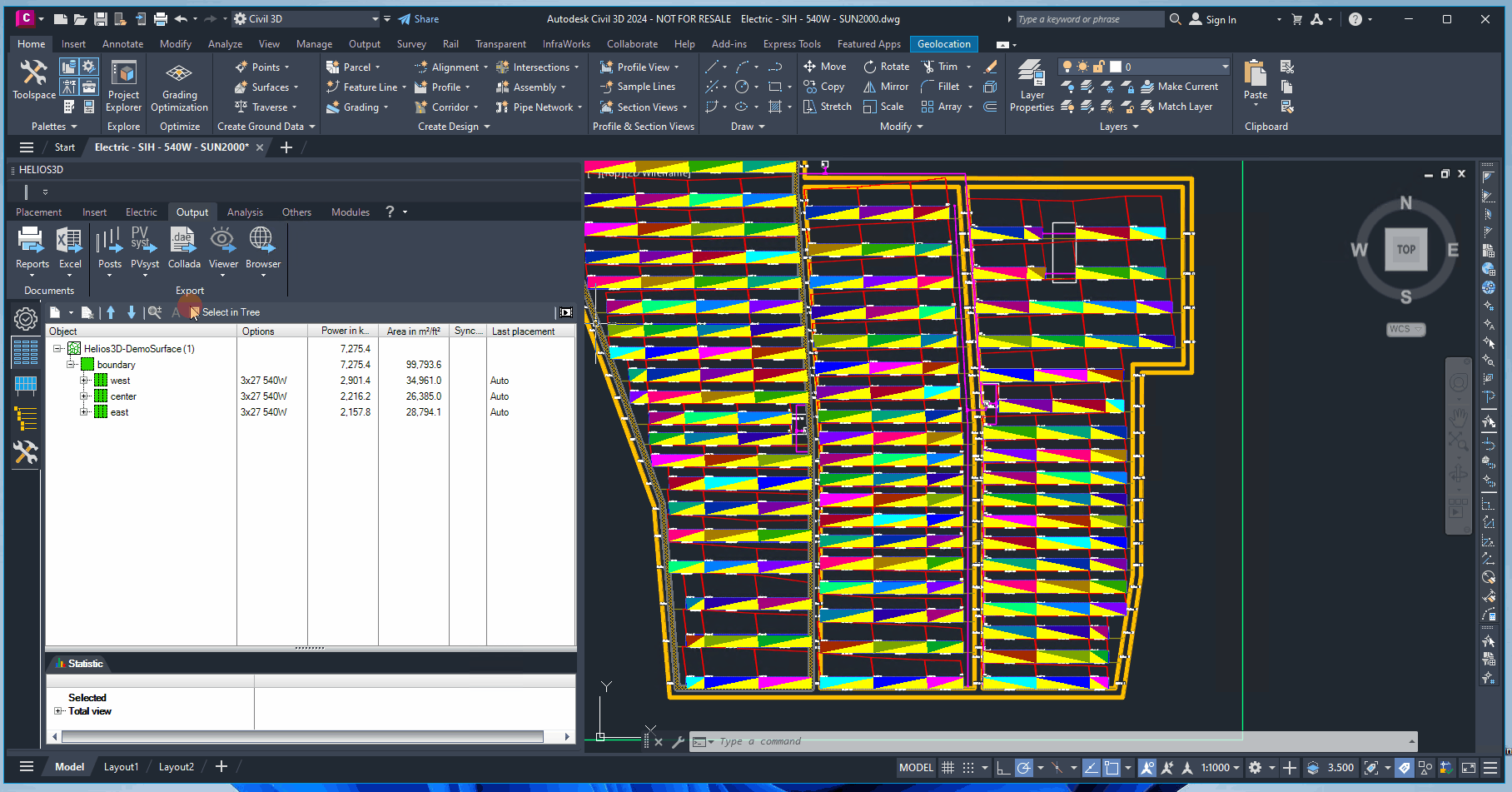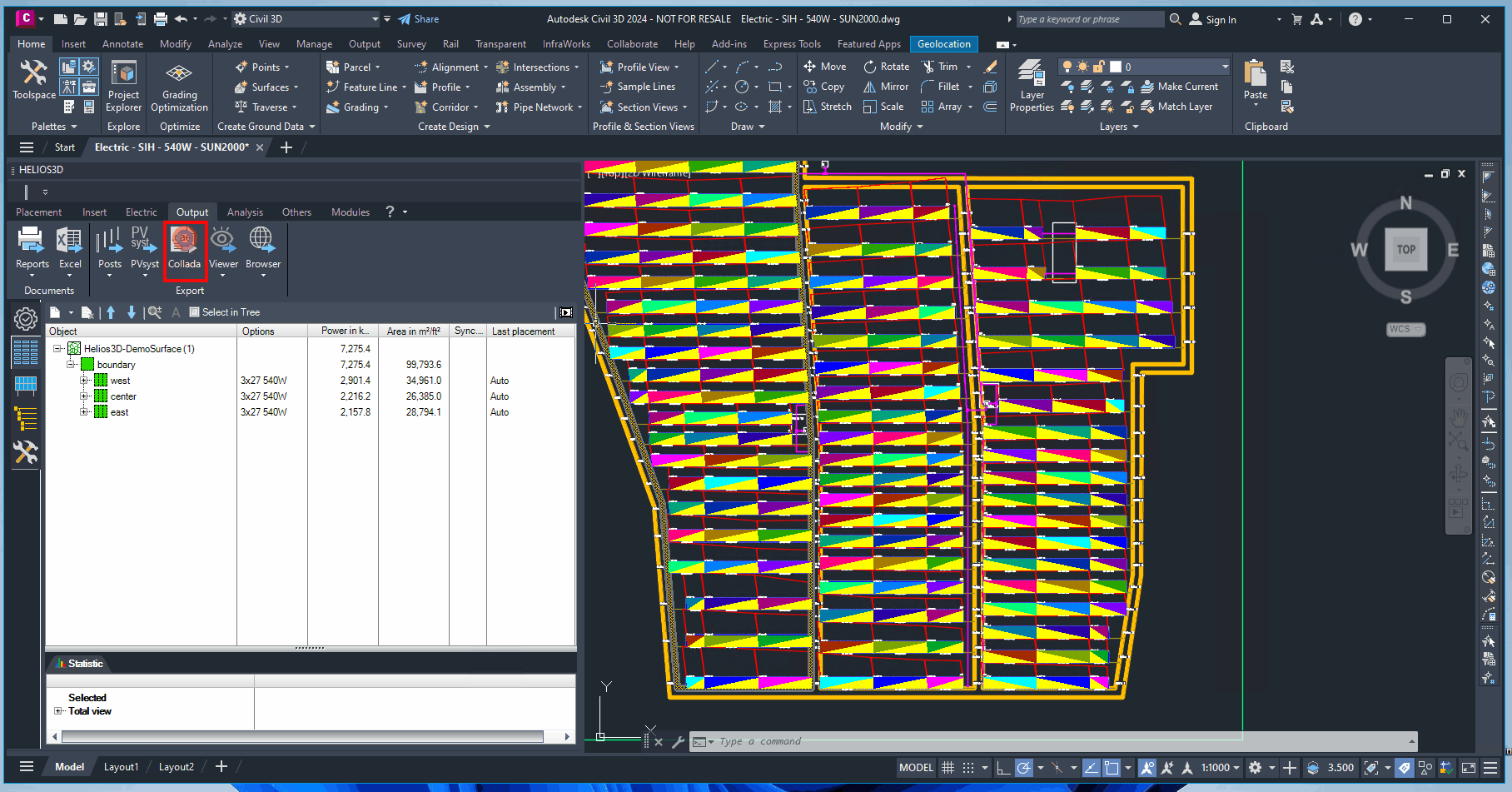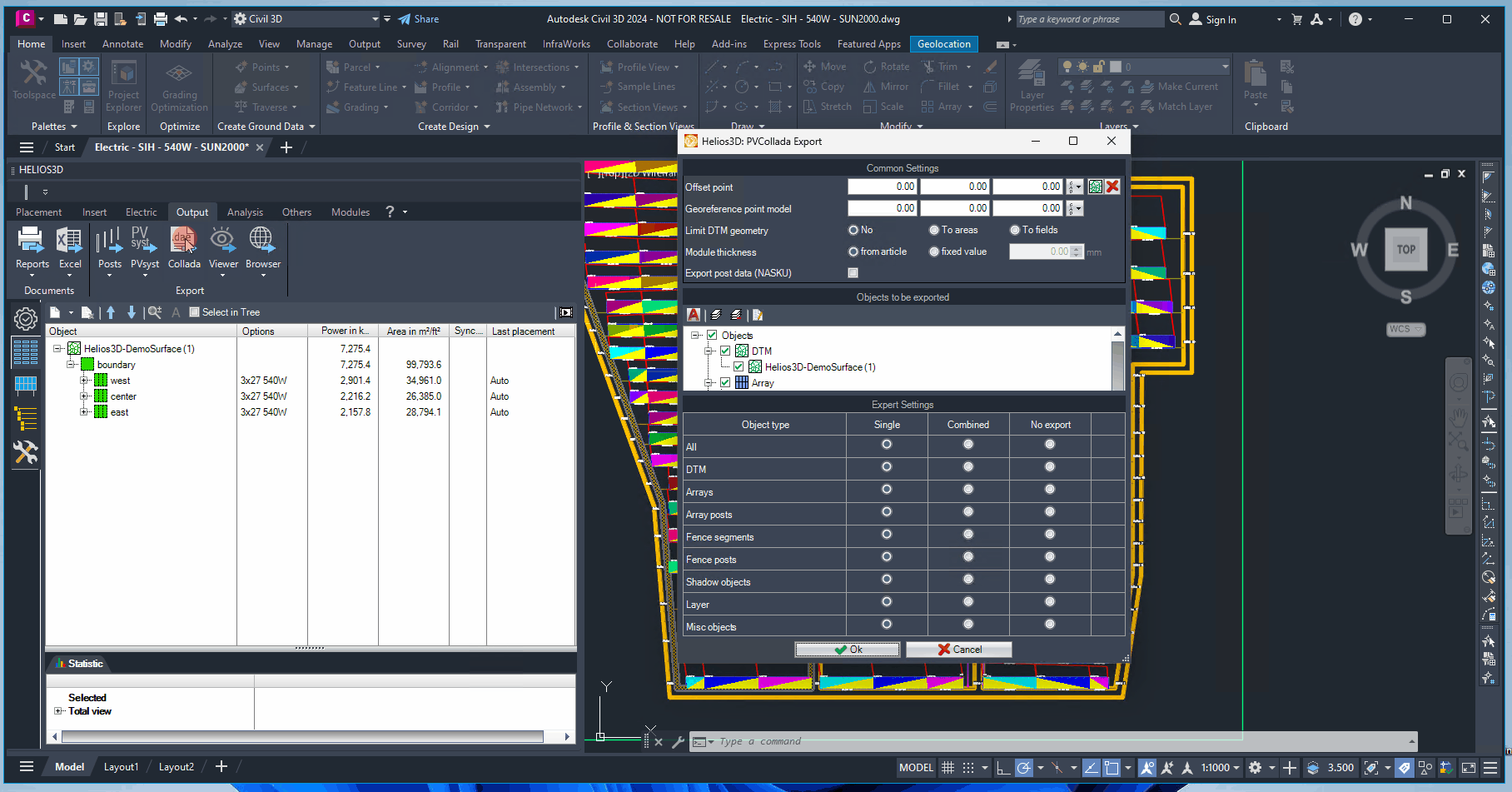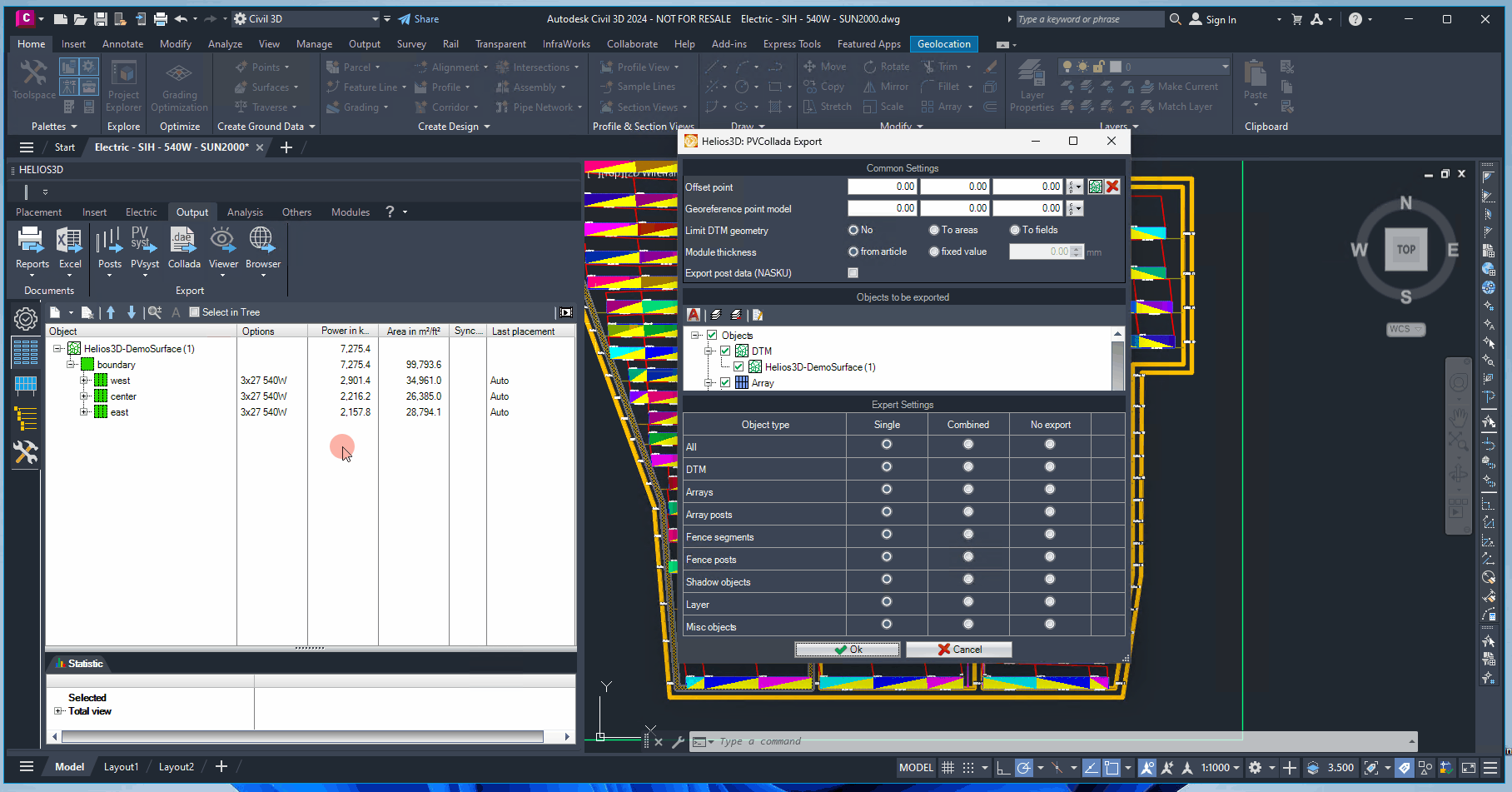
Offset point
Some software products can’t handle large drawing coordinates. This offset

allows exporting the center of the surface as origin point of the scene.
Georeference point model
Sets the reference point for the exported model, representing the GPS coordinates from the Helios 3D project settings. This information may be required by some target applications for their illumination models.
Limit DTM geometry
Can be used to reduce the exported scene size.
Module thickness
Some target applications use a different representation for modules.
Export post data (NASKU)
Writes the post data in the format defined for NASKU’s GPS-controlled GAYK rams to the export file.
These functions enable experimental analysis features for posts when activated during the new Viewer export.
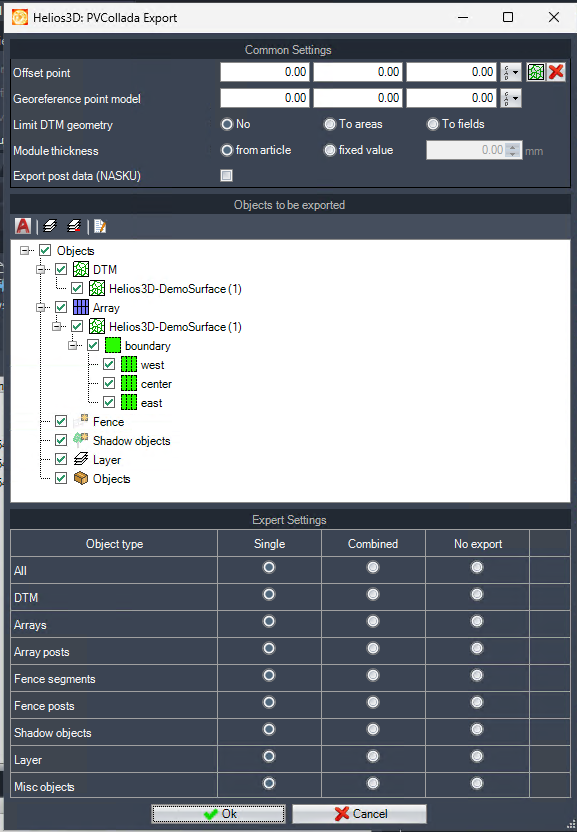
Objects to be exported / Expert Settings
The objects for the current export can be selected from the list. The expert settings further allow you to export all objects of a specific type either as individual objects or combined into a single block.
Start Helios 3D Viewer


Opens the dialogue to generate a 3D scene of the layout in an external viewer. You can move through this scene in flight mode.
The Helios 3D Viewer automatically installs and updates itself by this call.
Load Browser View
Opens the options dialog for generating a 3D environment including your planning area and displaying it in your default web browser. You can move through this 3D area in flight mode. For showing the array performance in browser view, you must use the corresponding option from the submenu after a yield calculation has been processed.
Attention: For this function your web browser must support WebGL!
Recommended Web Browsers: Firefox, Chrome
Browser Export with Array Performance

Generates the regular 3D scene and displays for any array its yearly performance, respectively the performance for the selected month.